|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
الكوكب (نجم)
اذهب إلى التنقل
اذهب إلى البحث
| كوكب | |
|---|---|
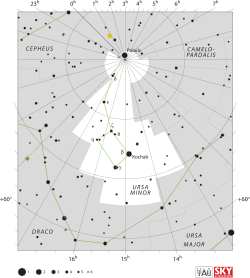
مكان نجم كوكب ( β ) في كوكبة الدب الأصغر .
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | الدب الأصغر |
| مطلع مستقيم | 14س 50د 42.32580ث[1] |
| الميل | ° +74 ′09 ″19.8142[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 2.08[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | K4 III[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +1.78[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +1.47[2] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +16.96[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | −32.61[1]+11.42[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 24.91 ± 0.12 د.ق |
| البعد | 130٫9 ± 0٫6 س.ض (40٫1 ± 0٫2 ف.ف) |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 2.2 ± 0.3[5] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 42.06 ± 0.91[6] نق☉ |
| ضياء | 390 ± 25[6] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 1.83[6] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 4,030[6] ك |
| معدنية (فلك) [Fe/H] | –0.29[6] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 8[7] كم/ثا |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Kochab, Kocab, Kochah, 7 Ursae Minoris, Al Kaukab al Shamaliyy, مسح بون الفلكي+74 595, فهرس النجوم الأساسية 550, فهرس النجوم 3373.00, فهرس هنري درابر 131873, هيباركوس 72607, فهرس النجم الساطع 5563, فهرس مرصد سميثسونيان للفيزياء الفلكية 8102.[8] | |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
الكوكب أو بيتا الدب الأصغر Beta Ursae Minoris اسمه التقليدي Kochab مشتق من الاسم العربي. وهو ثاني ألمع نجوم تقعر الدب الأصغر. وهو عبارة عملاق برتقالي يبعد 126.4 ± 2.5 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض. و ضياءه أكثر بـ 130 مرة من ضياء الشمس، وتبلغ درجة حرارة سطحة حوالي 4000 كلفن.[9]
وكوكب يقع في جوار فرقد وكلاهما مرئي بالعين المجردة، وكان كلاهما يشكل نجم القطب مابين 1500 قبل الميلاد حتى 500 بعد الميلاد.
انظر أيضا
المراجع
- ^ أ ب ت ث van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474، ص. 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ أ ب ت Johnson، H. L.؛ وآخرون (1966)، "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars"، Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory، ج. 4، Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J
- ^ Morgan، W. W.؛ Keenan، P. C. (1973)، "Spectral Classification"، Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 11، ص. 29، Bibcode:1973ARA&A..11...29M، DOI:10.1146/annurev.aa.11.090173.000333
- ^ Famaey، B.؛ وآخرون (يناير 2005)، "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 430، ص. 165–186، arXiv:astro-ph/0409579، Bibcode:2005A&A...430..165F، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272
- ^ Tarrant، N. J.؛ وآخرون (يونيو 2008)، "Oscillations in ß Ursae Minoris. Observations with SMEI"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 483، ص. L43–L46، arXiv:0804.3253، Bibcode:2008A&A...483L..43T، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:200809738
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Piau، L.؛ وآخرون (فبراير 2011)، "Surface convection and red-giant radius measurements"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 526، ص. A100، arXiv:1010.3649، Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.100P، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/201014442
- ^
Bernacca, P. L.; Perinotto, M. (1970)، "A catalogue of stellar rotational velocities"، Contributi Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova in Asiago، ج. 239، Bibcode:1970CoAsi.239....1B
{{استشهاد}}: صيانة الاستشهاد: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفين (link) - ^ "KOCHAB -- Variable Star"، SIMBAD، Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg، مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-04-14، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2012-01-11
- ^ eSky. "Kochab (Beta Ursae Minoris)". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2018-03-14. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2008-02-21.