|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
مستقبل ريتينويد أكس ألفا
اذهب إلى التنقل
اذهب إلى البحث
مستقبل ريتينويد أكس ألفا (بالإنجليزية: Retinoid X receptor alpha) (مختصره RXR-alpha), ويعرف كذلك مستقبل نووي عائلة 2، مجموعة ب، عضو 1 (بالإنجليزية: nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group B, member 1) (مختصره NR2B1) هو is a مستقبل نووي موجود عند الإنسان مشفر في المورثة RXRA.[1]
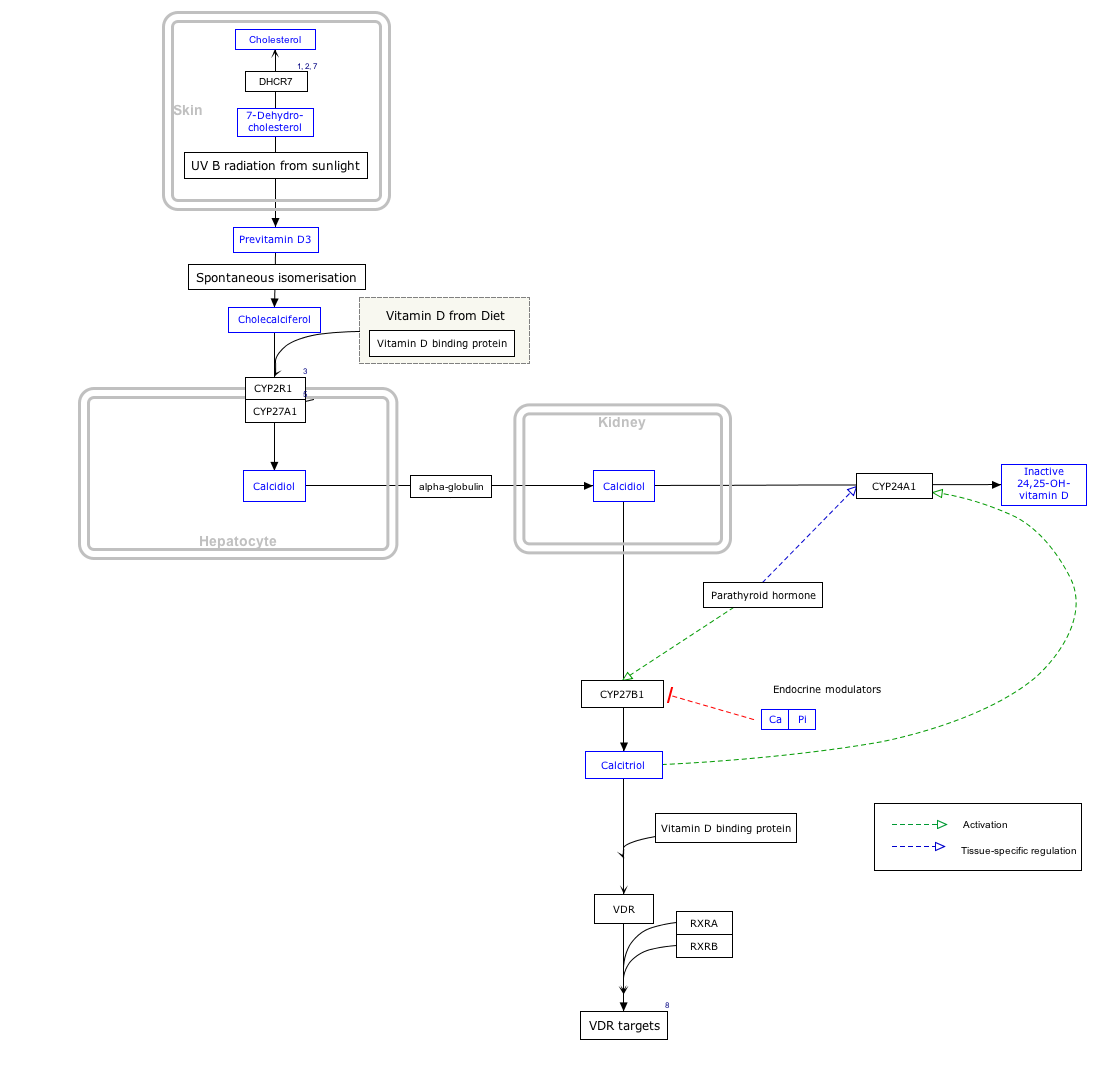
مخطط مسار تفاعلي
اضغط على المورثة أو البروتين أو المادة للذهاب إلى المقالة المتعلقة بها.[§ 1]
- ^ يمكن تعديل مخطط مسار التكوين التفاعلي في ويكيباثويز: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
| مستقبل ريتينويد أكس ألفا | |
|---|---|
| المعرفات | |
| الرمز | RXRA |
| أنتريه | 6256 |
| HUGO | 10477 |
| أوميم | 180245 |
| RefSeq | NM_002957 |
| يونيبروت | P19793 |
| بيانات أخرى | |
| الموقع الكروموسومي | Chr. 9 q34 |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
التفاعلات
أظهر مستقبل ريتنويد أكس ألفا تآثرات مع:
- BCL3,[2]
- BRD8,[3]
- CLOCK,[4]
- FXR[5]
- IGFBP3,[6]
- ITGB3BP,[7]
- LXR-β,[5]
- MyoD,[8]
- NCOA6,[9][10][11][12]
- NFKBIB,[13]
- NPAS2,[4]
- NRIP1,[14][15]
- NR4A1,[16]
- NCOA2,[17]
- NCOA3,[18]
- POU2F1,[19][20]
- PPARGC1A,[21]
- مستقبل منشط لمكاثر البيروكسيسوم النوع-غاما,[22][23][24]
- RNF8,[25]
- مستقبل حمض الريتينويك ألفا,[26][27]
- SHP,[28][29]
- TADA3L,[30]
- TBP,[31]
- TRIM24,[32][33]
- TR-β,[34][35]
- مستقبل كالسيتريول.[17][36]
طالع أيضا
المصادر
- ^ Mangelsdorf DJ، Ong ES، Dyck JA، Evans RM (مايو 1990). "Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway". Nature. ج. 345 ع. 6272: 224–9. Bibcode:1990Natur.345..224M. DOI:10.1038/345224a0. PMID:2159111.
- ^ Na SY، Choi HS، Kim JW، Na DS، Lee JW (1998). "Bcl3, an IkappaB protein, as a novel transcription coactivator of the retinoid X receptor". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 273 ع. 47: 30933–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.47.30933. PMID:9812988.
- ^ Monden T، Kishi M، Hosoya T، Satoh T، Wondisford FE، Hollenberg AN، Yamada M، Mori M (1999). "p120 acts as a specific coactivator for 9-cis-retinoic acid receptor (RXR) on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma/RXR heterodimers". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 13 ع. 10: 1695–703. DOI:10.1210/me.13.10.1695. PMID:10517671.
- ^ أ ب McNamara P، Seo SB، Rudic RD، Sehgal A، Chakravarti D، FitzGerald GA (2001). "Regulation of CLOCK and MOP4 by nuclear hormone receptors in the vasculature: a humoral mechanism to reset a peripheral clock". Cell. ج. 105 ع. 7: 877–89. DOI:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00401-9. PMID:11439184.
- ^ أ ب Seol W، Choi HS، Moore DD (1995). "Isolation of proteins that interact specifically with the retinoid X receptor: two novel orphan receptors". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 9 ع. 1: 72–85. DOI:10.1210/mend.9.1.7760852. PMID:7760852.
- ^ Liu B، Lee HY، Weinzimer SA، Powell DR، Clifford JL، Kurie JM، Cohen P (2000). "Direct functional interactions between insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and retinoid X receptor-alpha regulate transcriptional signaling and apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 275 ع. 43: 33607–13. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M002547200. PMID:10874028.
- ^ Li D، Desai-Yajnik V، Lo E، Schapira M، Abagyan R، Samuels HH (1999). "NRIF3 is a novel coactivator mediating functional specificity of nuclear hormone receptors". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 19 ع. 10: 7191–202. PMC:84712. PMID:10490654.
- ^ Froeschlé A، Alric S، Kitzmann M، Carnac G، Auradé F، Rochette-Egly C، Bonnieu A (1998). "Retinoic acid receptors and muscle b-HLH proteins: partners in retinoid-induced myogenesis". Oncogene. ج. 16 ع. 26: 3369–78. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1201894. PMID:9692544.
- ^ Lee SK، Anzick SL، Choi JE، Bubendorf L، Guan XY، Jung YK، Kallioniemi OP، Kononen J، Trent JM، Azorsa D، Jhun BH، Cheong JH، Lee YC، Meltzer PS، Lee JW (1999). "A nuclear factor, ASC-2, as a cancer-amplified transcriptional coactivator essential for ligand-dependent transactivation by nuclear receptors in vivo". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 274 ع. 48: 34283–93. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.48.34283. PMID:10567404.
- ^ Lee SK، Jung SY، Kim YS، Na SY، Lee YC، Lee JW (2001). "Two distinct nuclear receptor-interaction domains and CREB-binding protein-dependent transactivation function of activating signal cointegrator-2". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 15 ع. 2: 241–54. DOI:10.1210/me.15.2.241. PMID:11158331.
- ^ Kong HJ، Park MJ، Hong S، Yu HJ، Lee YC، Choi YH، Cheong J (2003). "Hepatitis B virus X protein regulates transactivation activity and protein stability of the cancer-amplified transcription coactivator ASC-2". Hepatology. ج. 38 ع. 5: 1258–66. DOI:10.1053/jhep.2003.50451. PMID:14578865.
- ^ Ko L، Cardona GR، Iwasaki T، Bramlett KS، Burris TP، Chin WW (2002). "Ser-884 adjacent to the LXXLL motif of coactivator TRBP defines selectivity for ERs and TRs". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 16 ع. 1: 128–40. DOI:10.1210/mend.16.1.0755. PMID:11773444.
- ^ Na SY، Kim HJ، Lee SK، Choi HS، Na DS، Lee MO، Chung M، Moore DD، Lee JW (1998). "IkappaBbeta interacts with the retinoid X receptor and inhibits retinoid-dependent transactivation in lipopolysaccharide-treated cells". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 273 ع. 6: 3212–5. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.6.3212. PMID:9452433.
- ^ Farooqui M، Franco PJ، Thompson J، Kagechika H، Chandraratna RA، Banaszak L، Wei LN (2003). "Effects of retinoid ligands on RIP140: molecular interaction with retinoid receptors and biological activity". Biochemistry. ج. 42 ع. 4: 971–9. DOI:10.1021/bi020497k. PMID:12549917.
- ^ L'Horset F، Dauvois S، Heery DM، Cavaillès V، Parker MG (1996). "RIP-140 interacts with multiple nuclear receptors by means of two distinct sites". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 16 ع. 11: 6029–36. PMC:231605. PMID:8887632.
- ^ Lin B، Kolluri SK، Lin F، Liu W، Han YH، Cao X، Dawson MI، Reed JC، Zhang XK (2004). "Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3". Cell. ج. 116 ع. 4: 527–40. DOI:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00162-X. PMID:14980220.
- ^ أ ب Zhang C، Baudino TA، Dowd DR، Tokumaru H، Wang W، MacDonald PN (2001). "Ternary complexes and cooperative interplay between NCoA-62/Ski-interacting protein and steroid receptor coactivators in vitamin D receptor-mediated transcription". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 276 ع. 44: 40614–20. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M106263200. PMID:11514567.
- ^ Chen H، Lin RJ، Schiltz RL، Chakravarti D، Nash A، Nagy L، Privalsky ML، Nakatani Y، Evans RM (1997). "Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300". Cell. ج. 90 ع. 3: 569–80. DOI:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80516-4. PMID:9267036.
- ^ Préfontaine GG، Walther R، Giffin W، Lemieux ME، Pope L، Haché RJ (1999). "Selective binding of steroid hormone receptors to octamer transcription factors determines transcriptional synergism at the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 274 ع. 38: 26713–9. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.38.26713. PMID:10480874.
- ^ Kakizawa T، Miyamoto T، Ichikawa K، Kaneko A، Suzuki S، Hara M، Nagasawa T، Takeda T، Mori Ji، Kumagai M، Hashizume K (1999). "Functional interaction between Oct-1 and retinoid X receptor". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 274 ع. 27: 19103–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19103. PMID:10383413.
- ^ Delerive P، Wu Y، Burris TP، Chin WW، Suen CS (2002). "PGC-1 functions as a transcriptional coactivator for the retinoid X receptors". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 277 ع. 6: 3913–7. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M109409200. PMID:11714715.
- ^ Tontonoz P، Graves RA، Budavari AI، Erdjument-Bromage H، Lui M، Hu E، Tempst P، Spiegelman BM (1994). "Adipocyte-specific transcription factor ARF6 is a heterodimeric complex of two nuclear hormone receptors, PPAR gamma and RXR alpha". Nucleic Acids Res. ج. 22 ع. 25: 5628–34. DOI:10.1093/nar/22.25.5628. PMC:310126. PMID:7838715.
- ^ Berger J، Patel HV، Woods J، Hayes NS، Parent SA، Clemas J، Leibowitz MD، Elbrecht A، Rachubinski RA، Capone JP، Moller DE (2000). "A PPARgamma mutant serves as a dominant negative inhibitor of PPAR signaling and is localized in the nucleus". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. ج. 162 ع. 1–2: 57–67. DOI:10.1016/S0303-7207(00)00211-2. PMID:10854698.
- ^ Gampe RT، Montana VG، Lambert MH، Miller AB، Bledsoe RK، Milburn MV، Kliewer SA، Willson TM، Xu HE (2000). "Asymmetry in the PPARgamma/RXRalpha crystal structure reveals the molecular basis of heterodimerization among nuclear receptors". Mol. Cell. ج. 5 ع. 3: 545–55. DOI:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80448-7. PMID:10882139.
- ^ Takano Y، Adachi S، Okuno M، Muto Y، Yoshioka T، Matsushima-Nishiwaki R، Tsurumi H، Ito K، Friedman SL، Moriwaki H، Kojima S، Okano Y (2004). "The RING finger protein, RNF8, interacts with retinoid X receptor alpha and enhances its transcription-stimulating activity". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 279 ع. 18: 18926–34. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M309148200. PMID:14981089.
- ^ Benkoussa M، Brand C، Delmotte MH، Formstecher P، Lefebvre P (2002). "Retinoic acid receptors inhibit AP1 activation by regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase and CBP recruitment to an AP1-responsive promoter". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 22 ع. 13: 4522–34. DOI:10.1128/MCB.22.13.4522-4534.2002. PMC:133906. PMID:12052862.
- ^ Bugge TH، Pohl J، Lonnoy O، Stunnenberg HG (1992). "RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors". EMBO J. ج. 11 ع. 4: 1409–18. PMC:556590. PMID:1314167.
- ^ Lee YK، Dell H، Dowhan DH، Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M، Moore DD (2000). "The orphan nuclear receptor SHP inhibits hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 and retinoid X receptor transactivation: two mechanisms for repression". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 20 ع. 1: 187–95. DOI:10.1128/MCB.20.1.187-195.2000. PMC:85074. PMID:10594021.
- ^ Brendel C، Schoonjans K، Botrugno OA، Treuter E، Auwerx J (2002). "The small heterodimer partner interacts with the liver X receptor alpha and represses its transcriptional activity". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 16 ع. 9: 2065–76. DOI:10.1210/me.2001-0194. PMID:12198243.
- ^ Zeng M، Kumar A، Meng G، Gao Q، Dimri G، Wazer D، Band H، Band V (2002). "Human papilloma virus 16 E6 oncoprotein inhibits retinoic X receptor-mediated transactivation by targeting human ADA3 coactivator". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 277 ع. 47: 45611–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M208447200. PMID:12235159.
- ^ Schulman IG، Chakravarti D، Juguilon H، Romo A، Evans RM (1995). "Interactions between the retinoid X receptor and a conserved region of the TATA-binding protein mediate hormone-dependent transactivation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 92 ع. 18: 8288–92. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.8288S. DOI:10.1073/pnas.92.18.8288. PMC:41142. PMID:7667283.
- ^ Thénot S، Henriquet C، Rochefort H، Cavaillès V (1997). "Differential interaction of nuclear receptors with the putative human transcriptional coactivator hTIF1". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 272 ع. 18: 12062–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.18.12062. PMID:9115274.
- ^ Lee WY، Noy N (2002). "Interactions of RXR with coactivators are differentially mediated by helix 11 of the receptor's ligand binding domain". Biochemistry. ج. 41 ع. 8: 2500–8. DOI:10.1021/bi011764. PMID:11851396.
- ^ Monden T، Wondisford FE، Hollenberg AN (1997). "Isolation and characterization of a novel ligand-dependent thyroid hormone receptor-coactivating protein". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 272 ع. 47: 29834–41. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.47.29834. PMID:9368056.
- ^ Jeyakumar M، Tanen MR، Bagchi MK (1997). "Analysis of the functional role of steroid receptor coactivator-1 in ligand-induced transactivation by thyroid hormone receptor". Mol. Endocrinol. ج. 11 ع. 6: 755–67. DOI:10.1210/mend.11.6.0003. PMID:9171239.
- ^ Baudino TA، Kraichely DM، Jefcoat SC، Winchester SK، Partridge NC، MacDonald PN (1998). "Isolation and characterization of a novel coactivator protein, NCoA-62, involved in vitamin D-mediated transcription". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 273 ع. 26: 16434–41. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.26.16434. PMID:9632709.