|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
سنوخس عصوي كاذب
Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli | |
|---|---|
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| المملكة: | الحيوانات |
| الشعبة: | الديدان المفلطحة |
| العمارة: | الديدان المخرمة أحادية المنشأ |
| الجنس: | سنوخس عصوي كاذب 1958 ,Yamaguti |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
الجنس سنوخس عصوي كاذب هو من المخرمات الأحادية المنشأ التي تنتمي إلى شعبة الديدان المفلطحة الطفيلية. كشف البحث في هذا الجنس عن وجود أكثر من 70 نوعا على غلاصم الأسماك البحرية وخصوصا على سمك الهامور الذي يعيش في المياه الساخنة و الشعاب المرجانية . أيضا، تم تسجيل أنواع من هذه الطفيليات في البحر الأبيض المتوسط .
الملامح الخارجية
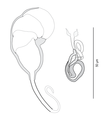
الأنواع التي تعود لجنس Pseudorhabdosynochus ديدان صغيرة يتراوح طولها بين 0.3–1 ملم. مثل جميع المخرمات الأحادية المنشأ، هي مسطحة وتملك أبسط التراكيب لجميع الديدان. تضم الجهة الخلفية على جهاز التثبيت واحد Monopisthocotylea . يتميز هذا الجنس عن باقي الأجناس التي تنتمي إلى فصيلة Diplectanidae بعضو السفاد الذي يأخذ شكلا فريدا من نوعه (أربع حجرات) ويلعب شكل المهبل دورا رئيسيا في التفريق بين أنواعه . وفقا لJustine عام 2007، الهيكل الرئيسي للمهبل كالتالي: بوق (Trompette) ، قناة رئيسية (Canal principal) ، غرفة رئيسية (Chambre principale) ، غرفة ثانية (Chambre secondaire)، قناة ثانوية (Canal secondaire). هذه الطفيليات هي حيوانات ثنائية الجنس خنثى و يتّم إخصاب البيض داخل الجسم وهي عملية تسمى الإخصاب الداخلي.
رواق
مضيف
الأنواع التي تعود إلى جنس Pseudorhabdosynochus تتطفل على غلاصم الأسماك البحرية التي تنتمي معظمها إلى فصيلة Epinephelidae نذكر منها خاصة سمك الهامور.أظهرت الدراسات الحالية أن جدري ، Mycteroperca ، Paranthias ، Cephalopholis و هامور (جنس) هي الأجناس المضيفة له. أنواع قليلة تم العثوع عليها في خلاصم Alphestes و Paralabrax . مثل معظم المخرمات الأحادية المنشأ التي تنتمي إلى فصيلة Diplectanidae، مختلف الأنواع المذكورة من جنس Pseudorhabdosynochus تعرف عموما بصرامة تعلقها بالمضيف أي تتطفل على نوع واحد من المضيف (spécificité stricte). من ناحية أخرى، يعدالهامور من الأسماك التي تؤوي عددا هاما من أنواع الطفيليات الخارجية خير مثال خلاصم سمكة الهامور Epinephelus maculatus التي تحتوي على 8 أنواع من جنس Pseudorhabdosynochus وأيضا خلاصم سمكة الهامور هامور مليبار (سبعة أنواع).
لائحة الأنواع
تم إصدار قوائم الأنواع من قبل Justine عام 2007 [1] و Kritsky & Beverley-Burton عام 1986 وهي كالتالي:
|
|
|
|
علم الأمراض وتربية الأحياء البحرية
لا توجد أي دراسة تبرز خطورة الأنواع التي تنتمي إلى Pseudorhabdosynochus على سمك الهامور لكن طفيليات المخرمات الأحادية المنشأ تلحق أضرارا واضحة بالأسماك وتتراوح هذه الأضرار ما بين المشاركة بالغذاء أو إحداث خدوش أو جروح في الأعضاء الجسمية التي تصيبها.
مراجع
- ^ .Justine: 2007 Parasite biodiversity in a coral reef fish: twelve species of monogeneans on the gills of the grouper Epinephelus maculatus (Perciformes:Serranidae) off New Caledonia, with a description of eight new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenea:Diplectanidae). Systematic Parasitology,66(2), 81-129
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز س ش Kritsky, D. C. & Beverley-Burton, M. 1986: The status of Pseudorhabdosynochus Yamaguti, 1958, and Cycloplectanum Oliver, 1968 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae). Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 99, 17-20. PDF
 نسخة محفوظة 05 مارس 2016 على موقع واي باك مشين.
نسخة محفوظة 05 مارس 2016 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- ^ Price, E. W. 1937: North American Monogenetic Trematodes. I. The superfamily Gyrodactyloidea. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 27, 146-164. PDF
 نسخة محفوظة 08 مارس 2016 على موقع واي باك مشين.
نسخة محفوظة 08 مارس 2016 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- ^ Bravo-Hollis, M. 1954: Diplectanum amplidiscatum n. sp., Trématode monogénétique des branchies d'un poisson marin. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 24, 37-41.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Mendoza-Franco، Edgar F.؛ Violante-González، Juan؛ Rojas Herrera، Agustín A. (2011). "Six new and one previously described species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenoidea, Diplectanidae) infecting the gills of groupers (Perciformes, Serranidae) from the Pacific coasts of Mexico and Panama". Journal of Parasitology. ج. 97 ع. 1: 20–35. DOI:10.1645/GE-2716.1. ISSN:0022-3395.
- ^ أ ب Justine، Jean-Lou (2007). "Pseudorhabdosynochus argus n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from Cephalopholis argus, P. minutus n. sp. and Diplectanum nanus n. sp. from C. sonnerati and other monogeneans from Cephalopholis spp. (Perciformes: Serranidae) off Australia and New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 68 ع. 3: 195–215. DOI:10.1007/s11230-007-9096-4. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د Justine، Jean-Lou (2007). "Parasite biodiversity in a coral reef fish: twelve species of monogeneans on the gills of the grouper Epinephelus maculatus (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia, with a description of eight new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenea: Diplectanidae)". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 66 ع. 2: 81–129. DOI:10.1007/s11230-006-9057-3.
- ^ Sigura، Aude؛ Chauvet، Claude؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2007). "Pseudorhabdosynochus bacchus sp. nov. (Monogenea, Diplectanidae) from Epinephelus coeruleopunctatus (Perciformes, Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Acta Parasitologica. ج. 52 ع. 3. DOI:10.2478/s11686-007-0028-x. ISSN:1896-1851.
- ^ أ ب Oliver, G. 1984: Description de deux nouvelles espèces du genre Cycloplectanum Oliver, 1968 (Monogenea, Monopisthocotylea, Diplectanidae). Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 59, 31-39.
- ^ أ ب Oliver, G. & Paperna, I. 1984: Diplectanidae Bychowsky, 1957 (Monogenea, Monopisthocotylea), parasites de Perciformes de Méditerranée orientale, de la mer Rouge et de l'océan Indien. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 4° série, 6, section A, 49-65.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Neifar، Lassad؛ Euzet، Louis (2007). "Five new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the gills of Epinephelus costae (Teleostei: Serranidae)" (PDF). Folia Parasitologica. ج. 54 ع. 2: 117–128. DOI:10.14411/fp.2007.017. ISSN:0015-5683. مؤرشف من الأصل (PDF) في 2020-09-18.

- ^ أ ب Hinsinger، Damien D.؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2006). "The 'Pseudorhabdosynochus cupatus group' (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) on Epinephelus fasciatus, E. howlandi, E. rivulatus and E. merra (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia, with descriptions of Pseudorhabdosynochus cyathus n. sp. and P. calathus n. sp". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 64 ع. 2: 69–90. DOI:10.1007/s11230-005-9018-2. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Justine، Jean-Lou (2005). "Species of Pseudorhabdosynochus Yamaguti, 1958 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from Epinephelus fasciatus and E. merra (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia and other parts of the Indo-Pacific Ocean, with a comparison of measurements of specimens prepared using different methods, and a description of P. caledonicus n. sp". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 62 ع. 1: 1–37. DOI:10.1007/s11230-005-5480-0. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Vidal-Martínez, V. M. & Mendoza-Franco, E. F. 1998: Pseudorhabdosynochus capurroi sp. n. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the gills of Mycteroperca bonaci (Pisces: Serranidae) of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Folia Parasitologica, 45, 221-224. Article PDF
 "نسخة مؤرشفة". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2017-02-08. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2015-03-16.
"نسخة مؤرشفة". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2017-02-08. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2015-03-16.{{استشهاد ويب}}: صيانة الاستشهاد: BOT: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ أ ب ت ث Sigura, A. & Justine, J.-L. 2008: Monogeneans of the speckled blue grouper, Epinephelus cyanopodus (Perciformes, Serranidae), from off New Caledonia, with a description of four new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus and one new species of Laticola (Monogenea: Diplectanidae), and evidence of monogenean faunal changes according to the size of fish. Zootaxa, 1695, 1-44.
- ^ Zhang, J. Y., Yang, T. B. & Liu, L. (2001). [Monogeneans of Chinese marine fishes] (in Chinese). Beijing: Agriculture Press.
- ^ Bu, S. S. H., Leong, T. S., Wong, S. Y., Woo, Y. S. N. & Foo, R. W. T. 1999: Three diplectanid monogeneans from marine finfish (Epinephelus spp.) in the Far East. Journal of Helminthology, 73, 301-312. دُوِي:10.1017/S0022149X99000505
- ^ أ ب ت Schoelinck، Charlotte؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2011). "Four species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the camouflage grouper Epinephelus polyphekadion (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 79 ع. 1: 41–61. DOI:10.1007/s11230-010-9289-0. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ أ ب ت Young، P. C. (1969). "Some Monogenoideans of the Family Diplectanidae Bychowsky, 1957 from Australian Teleost Fishes". Journal of Helminthology. ج. 43 ع. 1–2: 223. DOI:10.1017/S0022149X00004053. ISSN:0022-149X.
- ^ Yamaguti, S. 1938: Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 24. Trematodes of fishes, V. Japanese Journal of Zoology, 8, 15-74.
- ^ أ ب Justine، Jean-Lou؛ Henry، Émilie (2010). "Monogeneans from Epinephelus chlorostigma (Val.) (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia, with the description of three new species of diplectanids". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 77 ع. 2: 81–105. DOI:10.1007/s11230-010-9263-x. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Santos، Cláudia Portes؛ Buchmann، Kurt؛ Gibson، David I. (2000). "Pseudorhabdosynochus spp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the gills of Epinephelus spp. in Brazilian waters". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 45 ع. 2: 145–153. DOI:10.1023/A:1006232029426. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Justine، Jean-Lou (2005). "Pseudorhabdosynochus hirundineus n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from Variola louti (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 62 ع. 1: 39–45. DOI:10.1007/s11230-005-5481-z. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Justine، Jean-Lou (2008). "Pseudorhabdosynochus inversus sp. nov. (Monogenea, Diplectanidae) from the halfmoon grouper Epinephelus rivulatus (Perciformes, Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Acta Parasitologica. ج. 53 ع. 4. DOI:10.2478/s11686-008-0057-0. ISSN:1896-1851.
- ^ Knoff، Marcelo؛ Cohen، Simone Chinicz؛ Cárdenas، Melissa Querido؛ Cárdenas-Callirgos، Jorge M.؛ Gomes، Delir Corrêa (2015). "A new species of diplectanid (Monogenoidea) from Paranthias colonus (Perciformes, Serranidae) off Peru". Parasite. ج. 22: 11. DOI:10.1051/parasite/2015011. PMID:25754099. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2015-09-24.

- ^ Zeng، Bijian؛ Yang، Tingbao (2006). "Description of Pseudorhabdosynochus justinei n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) and redescription of P. vagampullum (Young, 1969) Kritsky & Beverley-Burton, 1986 from the gills of the longfin grouper Epinephelus quoyanus (Valenciennes) (Perciformes: Serranidae) in Dapeng Bay, South China Sea". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 66 ع. 3: 223–235. DOI:10.1007/s11230-006-9067-1. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Dyer، William G.؛ Williams، Ernest H.؛ Bunkley-Williams، Lucy (1995). "Pseudorhabdosynochus kritskyi n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) on Gag from the Gulf of Mexico". Journal of Aquatic Animal Health. ج. 7 ع. 4: 337–340. DOI:10.1577/1548-8667(1995)007<0337:KNSDOG>2.3.CO;2. ISSN:0899-7659.
- ^ Beverley-Burton، Mary؛ Suriano، Delia Mabel (1981). "A revision of Cycloplectanum Oliver, 1968 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) and descriptions of C.hongkongensis n.sp. and C.lantauensis n.sp. from Epinephelus spp. (Serranidae) in the South China Sea". Canadian Journal of Zoology. ج. 59 ع. 7: 1276–1285. DOI:10.1139/z81-180. ISSN:0008-4301.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Justine, J.-L. & Sigura, A. 2007: Monogeneans of the malabar grouper Epinephelus malabaricus (Perciformes, Serranidae) off New Caledonia, with a description of six new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus (Monogenea: Diplectanidae). Zootaxa, 1543, 1-44.
- ^ Aljoshkina, L. D. 1984: [New species of the family Diplectanidae (Monogenea) in the South-West Atlantic]. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 63, 1253-1256.
- ^ Laird، Marshall (1958). "Parasites of South Pacific fishes II. Diplectanum melanesiensis n. sp., a monogenetic trematode from Fiji and the New Hebrides". Canadian Journal of Zoology. ج. 36 ع. 2: 167–173. DOI:10.1139/z58-017. ISSN:0008-4301.
- ^ Dyer، William G.؛ Williams، Ernest H.؛ Bunkley-Williams، Lucy (1994). "Pseudorhabdosynochus monaensis n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) on Rock Hind from Mona Island, Puerto Rico". Journal of Aquatic Animal Health. ج. 6 ع. 1: 59–63. DOI:10.1577/1548-8667(1994)006<0059:PMNSMD>2.3.CO;2. ISSN:0899-7659.
- ^ أ ب Justine، Jean-Lou (2008). "Two new species of Pseudorhabdosynochus Yamaguti, 1958 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the deep-sea grouper Epinephelus morrhua (Val.) (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 71 ع. 2: 145–158. DOI:10.1007/s11230-008-9156-4. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Justine، Jean-Lou؛ Vignon، Matthias (2008). "Monogeneans of the grouper Epinephelus tauvina (Perciformes, Serranidae) off Moorea, French Polynesia, with a description of Pseudorhabdosynochus pai n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae)". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 72 ع. 2: 113–125. DOI:10.1007/s11230-008-9159-1. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Schoelinck، Charlotte؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2011). "Pseudorhabdosynochus quadratus n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the white-streaked grouper Epinephelus ongus (Bloch) (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 79 ع. 1: 77–80. DOI:10.1007/s11230-011-9295-x. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Yamaguti, S. (1968). Monogenetic Trematodes of Hawaiian Fishes. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
- ^ Chaabane، Amira؛ Neifar، Lassad؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2015). "Pseudorhabdosynochus regius n. sp. (Monogenea, Diplectanidae) from the mottled grouper Mycteroperca rubra (Teleostei) in the Mediterranean Sea and Eastern Atlantic". Parasite. ج. 22: 9. DOI:10.1051/parasite/2015005. ISSN:1776-1042. PMID:25674913. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2015-09-24.

- ^ Oliver، Guy (1986). "Cycloplectanum riouxi n. sp., une nouvelle espèce de Diplectanidae (Monogenea, Monopisthocotylea) parasite d'Epinephelus guaza (Linnaeus, 1758) (Pisces, Serranidae)". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 8 ع. 4: 317–322. DOI:10.1007/BF00009739. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Justine، Jean-Lou (2009). "A redescription of Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli (Yamaguti, 1938), the type-species of Pseudorhabdosynochus Yamaguti, 1958 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae), and the description of P. satyui n. sp. from Epinephelus akaara off Japan". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 72 ع. 1: 27–55. DOI:10.1007/s11230-008-9171-5.
- ^ Yamaguti, S. 1953: Parasitic worms mainly from Celebes. Part 2. Monogenetic trematodes of fishes. Acta Medicinae Okayama, 8, 203-256 + 209 Pl. Article نسخة محفوظة 4 مارس 2016 على موقع واي باك مشين. PDF نسخة محفوظة 9 فبراير 2015 على موقع واي باك مشين.
 "نسخة مؤرشفة". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-03-04. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2015-03-16.
"نسخة مؤرشفة". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-03-04. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2015-03-16.{{استشهاد ويب}}: صيانة الاستشهاد: BOT: original URL status unknown (link)[وصلة مكسورة] - ^ Yang، Tingbao؛ Zeng، Bijian؛ Gibson، David I. (2005). "Description of Pseudorhabdosynochus shenzhenensis n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) and redescription of P. serrani Yamaguti, 1953 from Epinephelus coioides off Dapeng Bay, Shenzhen, China". Journal of Parasitology. ج. 91 ع. 4: 808–813. DOI:10.1645/GE-518R.1. ISSN:0022-3395.
- ^ Yang، Tingbao؛ Gibson، David I.؛ Zeng، Bijian (2005). "Pseudorhabdosynochus summanoides n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from Epinephelus coioides in Dapeng Bay, South China Sea, with observations on several similar species of Pseudorhabdosynochus Yamaguti, 1958". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 62 ع. 3: 221–239. DOI:10.1007/s11230-005-5497-4. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Hinsinger، Damien D.؛ Justine، Jean-Lou (2006). "Pseudorhabdosynochus venus n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from Epinephelus howlandi (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia". Systematic Parasitology. ج. 63 ع. 2: 153–158. DOI:10.1007/s11230-005-9012-8. ISSN:0165-5752.
- ^ Vidal-Martínez, V. M., Aguirre-Macedo, L. & Mendoza-Franco, E. F. 1997: Pseudorhabdosynochus yucatanensis sp. n. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) from the gills of the red grouper Epinephelus morio (Pisces: Serranidae) of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Folia Parasitologica, 44, 274-278. PDF
 نسخة محفوظة 02 أبريل 2015 على موقع واي باك مشين.
نسخة محفوظة 02 أبريل 2015 على موقع واي باك مشين.
| Pseudorhabdosynochus في المشاريع الشقيقة: | |