إنديلوكسازين
إنديلوكسازين أو إلين أو نوين هو دواء مضاد للاكتئاب ومنشط لوظائف لدماغ [1] [2] يُباع في في اليابان وكوريا الجنوبية بواسطة شركة يامنوتشي للتصنيعات الدوائية لعلاج الأعراض النفسية المرتبطة بأمراض الأوعية الدماغية، والاكتئاب الناتج من السكتة الدماغية، والاضطرابات العاطفية، وانعدام الإرادة.[3][4] بدأ تسويق الدواء من عام 1988[4] إلى عام 1998، عندما سُحب من الأسواق بسبب نقص الفعالية.[5]
| إنديلوكسازين | |
|---|---|
| الاسم النظامي | |
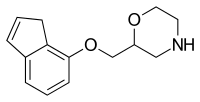
| 2-(3H-Inden-4-yloxymethyl)morpholine | |
| اعتبارات علاجية | |
| مرادفات | CI-874, YM-08054 |
| معرّفات | |
| CAS | 60929-23-9 |
| ك ع ت | None |
| بوب كيم | CID 3704 |
| كيم سبايدر | 3576 |
| المكون الفريد | 834M09R1KM |
| كيوتو | D08077 |
| ترادف | CI-874, YM-08054 |
| بيانات كيميائية | |
| الصيغة الكيميائية | C14H17NO2 |
| الكتلة الجزيئية | 231.290 g/mol |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
يعمل إنديلوكسازين كمحفز لإفراز السيروتونين، ومثبط لإعادة امتصاص النورإبينفرين، ومضاد لمستقبلات NMDA.[6][7] كما وُجد أنه يعزز من إطلاق الأسيتيل كولين في الدماغ الأمامي للفئران من خلال تنشيط مستقبلات 5-HT <sub id="mwGw">4</sub> ومن خلال عمله كمُحفز لإفراز للسيروتونين.[8][9][10] ويتميز هذا الدواء بآثاره المنشطة للذهن،[11][12]، وآثاره الوقائية للخلايا العصبية، [13][14][15][16] وآثاره المضادة للاختلاج،[17] وتأثيراته المضادة للاكتئاب في النماذج الحيوانية.[1][6]
المراجع
- ^ أ ب "Syntheses of (+/-)-2-[(inden-7-yloxy)methyl]morpholine hydrochloride (YM-08054, indeloxazine hydrochloride) and its derivatives with potential cerebral-activating and antidepressive properties". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. ج. 33 ع. 9: 3766–74. سبتمبر 1985. DOI:10.1248/cpb.33.3766. PMID:4092278.
- ^ "Determination of indeloxazine, a new antidepressant agent, in human plasma by gas-liquid chromatography with electron-capture detection". Journal of Chromatography. ج. 272 ع. 1: 176–80. يناير 1983. DOI:10.1016/s0378-4347(00)86115-0. PMID:6841538.
- ^ Index nominum, international drug ... - Google Books. 2000. ISBN:978-3-88763-075-1. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2020-04-14.
- ^ أ ب r Ganellin، C؛ j Triggle، D؛ MacDonald، F. (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents - Google Books. ISBN:978-0-412-46630-4. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2020-03-12.
- ^ Hayashi، K؛ Hashimoto، K؛ Yanagi، M؛ Umeda، T؛ Hama، R (8 أغسطس 1998). "Drug approval in Japan questioned". Lancet. ج. 352 ع. 9126: 491. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)79232-1. PMID:9708787.
- ^ أ ب "Neurochemical and behavioral characterization of potential antidepressant properties of indeloxazine hydrochloride". Neuropharmacology. ج. 37 ع. 9: 1169–76. سبتمبر 1998. DOI:10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00009-4. PMID:9833647. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2018-09-16.
- ^ "Effects of several cerebroprotective drugs on NMDA channel function: evaluation using Xenopus oocytes and [3H]MK-801 binding". European Journal of Pharmacology. ج. 207 ع. 2: 119–28. يونيو 1991. DOI:10.1016/0922-4106(91)90086-w. PMID:1652446.
- ^ Peñas-Cazorla، Raúl؛ Vilaró، M. Teresa (2014). "Serotonin 5-HT4 receptors and forebrain cholinergic system: receptor expression in identified cell populations". Brain Structure and Function. ج. 220 ع. 6: 3413–3434. DOI:10.1007/s00429-014-0864-z. ISSN:1863-2653.
- ^ "Facilitation of acetylcholine release in rat frontal cortex by indeloxazine hydrochloride: involvement of endogenous serotonin and 5-HT4 receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. ج. 356 ع. 6: 712–20. ديسمبر 1997. DOI:10.1007/pl00005110. PMID:9453456. مؤرشف من الأصل في 1999-10-08.
- ^ "Possible involvement of central cholinergic system in ameliorating effects of indeloxazine, a cerebral activator, on disturbance of learning behavior in rats". Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. ج. 18 ع. 3: 603–13. مايو 1994. DOI:10.1016/0278-5846(94)90016-7. PMID:8078992.
- ^ "Comparison of the effects of bifemelane hydrochloride and indeloxazine hydrochloride on scopolamine hydrobromide-induced impairment in radial maze performance". Clinical Therapeutics. ج. 10 ع. 6: 704–11. 1988. PMID:3219685.
- ^ "Cerebral activating properties of indeloxazine hydrochloride". Neuropharmacology. ج. 26 ع. 7A: 761–70. يوليو 1987. DOI:10.1016/0028-3908(87)90239-5. PMID:3627384.
- ^ "Comparison of the effects of bifemelane hydrochloride, idebenone and indeloxazine hydrochloride on ischemia-induced depletion of brain acetylcholine levels in gerbils". Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. ج. 61 ع. 2: 285–8. 1988. PMID:3187197.
- ^ "Protective effects of indeloxazine hydrochloride on cerebral ischemia in animals". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie. ج. 290 ع. 1: 16–24. نوفمبر 1987. PMID:3446040.
- ^ "Anti-hypoxic and anti-ischemic actions of indeloxazine hydrochloride and its optical isomers: possible involvement of cerebral energy metabolism". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie. ج. 324: 33–46. 1993. PMID:8297184.
- ^ "Effects of indeloxazine hydrochloride (YM-08054) on anoxia". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie. ج. 286 ع. 2: 272–81. أبريل 1987. PMID:3592867.
- ^ "Effects of indeloxazine HCl on kindled amygdaloid seizures in rats: comparison with the effects of phenytoin, diazepam, ethanol, and imipramine". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. ج. 45 ع. 2: 445–50. يونيو 1993. DOI:10.1016/0091-3057(93)90263-s. PMID:8327550.
| في كومنز صور وملفات عن: إنديلوكسازين |