|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
العذارى (نجم)
| العذارى | |
|---|---|
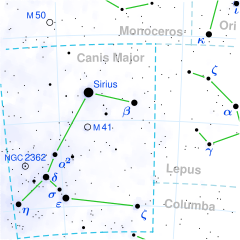
موقع نجم العذارى في الكوكبة.
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | الكلب الأكبر |
| مطلع مستقيم | 06س 58د 37.6ث |
| الميل | ° –28 ′58 ″19 |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 1.50[1] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | B2II[2] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | –0.93[1] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | –0.21[1] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +27.3 كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | +2.63[3][4]+2.29[3][4] |
| التزيح (π) | 7.57 ± 0.57 د.ق |
| البعد | 430 ± 30 س.ض (132 ± 10 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | –4.8[5] |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 12.6 ± 1.0[2] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 13.9[6] نق☉ |
| ضياء | 38,700[7] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 3.31[7] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 22,200[7] ك |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 25[8] كم/ثا |
| عمر | 22.5 ± 2.6[2] م.سنة |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Adhara, Adharaz, Undara, ε CMa, 21 CMa, فهرس النجوم 5654, CoD −28° 3666, FK5 268, HD 52089, هيباركوس 33579, HR 2618, SAO 172676. | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| سيمباد | بيانات |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
أو إبسلون الكلب الأكبر Epsilon Canis Majoris اسمه التقليدي Adhara مشتق من الاسم العربي. وهو نجم مزدوج في كوكبة الكلب الأكبر وهو ثاني ألمع نجم في الكوكبة ومن ألمع النجوم في السماء.
يبعد العذارى 430 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض.[9] يبلغ القدر الظاهري للنجم الرئيسي +1.5 وينتمي إلى الفئة الطيفية B2. وتصل درجة حرارة سطحه 25000 كلفن ويبث إشعاع كلي يساوي 20000 ضعف من الإشعاع الشمسي الكلي. ويقدر أنه لو كان بعد هذا النجم عنا بنفس بعد الشعرى اليمانية فإنه سيكون أكثر تألقا ب 15 من تألق الزهرة في السماء. كما أنه واحد من أكثر النجوم إصداراً للأشعة فوق البنفسجية في السماء.
يبلغ القدر الظاهري لشريكه +7.5 ويتموضع بزاوية 161 درجة عن الرئيسي.
انظر أيضا
المراجع
- ^ أ ب ت Ducati، J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. ج. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ أ ب ت Tetzlaff، N.؛ Neuhäuser، R.؛ Hohle، M. M. (يناير 2011)، "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 410، ص. 190–200، arXiv:1007.4883، Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T، DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x
- ^ أ ب Perryman، M. A. C.؛ Lindegren، L.؛ Kovalevsky، J.؛ Hoeg، E.؛ Bastian، U.؛ Bernacca، P. L.؛ Crézé، M.؛ Donati، F.؛ Grenon، M.؛ Grewing، M.؛ Van Leeuwen، F.؛ Van Der Marel، H.؛ Mignard، F.؛ Murray، C. A.؛ Le Poole، R. S.؛ Schrijver، H.؛ Turon، C.؛ Arenou، F.؛ Froeschlé، M.؛ Petersen، C. S.؛ وآخرون (1997). "The HIPPARCOS Catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics 323. ج. 323: L49–L52. Bibcode:1997A&A...323L..49P.
- ^ أ ب van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474، ص. 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ Snow، Theodore P.؛ Lamers، Henny J. G. L. M.؛ Lindholm، Douglas M.؛ Odell، Andrew P. (1994). "An atlas of ultraviolet P Cygni profiles". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. ج. 95: 163. Bibcode:1994ApJS...95..163S. DOI:10.1086/192099.
- ^ Underhill، A. B.؛ وآخرون (نوفمبر 1979)، "Effective temperatures, angular diameters, distances and linear radii for 160 O and B stars"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 189، ص. 601–605، Bibcode:1979MNRAS.189..601U، DOI:10.1093/mnras/189.3.601
- ^ أ ب ت Lyubimkov، L. S.؛ Rostopchin، S. I.؛ Lambert، D. L. (يونيو 2004)، "Surface abundances of light elements for a large sample of early B-type stars - III. An analysis of helium lines in spectra of 102 stars"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 351، ص. 745–767، Bibcode:2004MNRAS.351..745L، DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07825.x
- ^ Abt، Helmut A.؛ Levato، Hugo؛ Grosso، Monica (يوليو 2002)، "Rotational Velocities of B Stars"، The Astrophysical Journal، ج. 573، ص. 359–365، Bibcode:2002ApJ...573..359A، DOI:10.1086/340590.
- ^ Adhara (Epsilon Canis Majoris) نسخة محفوظة 21 أكتوبر 2017 على موقع واي باك مشين.
| العذارى في المشاريع الشقيقة: | |